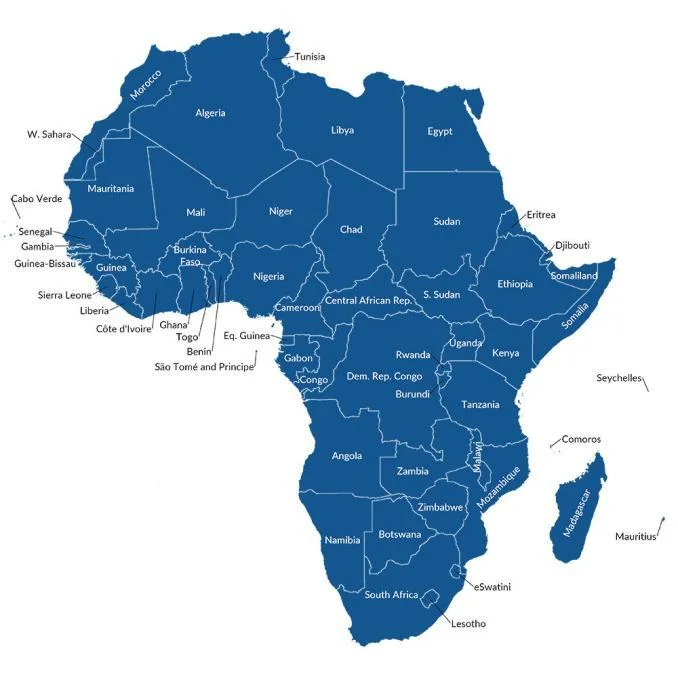
Countries in Africa
Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros Islands, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, eSwatini (formerly Swaziland), Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, Western Sahara, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
About Africa
Africa is the world’s second-largest continent, covering an area of approximately 30.2 million square kilometers or 11.7 million square miles. It is located south of Europe and the Mediterranean Sea, west of Asia, and east of the Atlantic Ocean and the Americas. The continent is home to 54 countries and is characterized by diverse landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to lush rainforests, and a rich cultural heritage that includes a multitude of languages, religions, and traditions.
Facts about Africa continent |
|
|---|---|
| Size | Africa is the second-largest continent, covering approximately 30.2 million square kilometers. |
| Countries | Africa is home to 54 recognized sovereign states and several dependent territories. |
| Population | The continent has an estimated population of 1.34 billion people, making it the world’s second-most populous continent after Asia. |
| Languages | Africa is home to more than 2,000 languages, with Arabic, Swahili, and Hausa being among the most widely spoken. |
| Landmarks and attractions | Africa boasts many natural landmarks and attractions, including the Sahara desert, Victoria Falls, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the Serengeti National Park. |
| Biodiversity and wildlife | Africa is known for its diverse wildlife, with some of the most iconic and endangered species, such as elephants, lions, and gorillas, calling the continent home. |
| Political divisions and borders | The continent is divided into five regions: Northern Africa, Western Africa, Central Africa, Eastern Africa, and Southern Africa. |
| Colonial history and legacy | Africa has a complicated colonial history that has left lasting legacies, including the imposition of artificial borders that do not always reflect the continent’s cultural, linguistic, and ethnic diversity. |
| Economic challenges and opportunities | Africa faces significant economic challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and inequality, but it also has vast potential, with abundant natural resources and a young and growing population. |
Physical Characteristics of Africa
- Landforms: Africa has a variety of landforms, including plateaus, mountains, valleys, and deserts. The continent is home to the world’s largest hot desert, the Sahara, which spans 11 countries in North Africa. Other notable landforms include the Ethiopian Highlands, the Atlas Mountains, the Drakensberg Range, and the Great Rift Valley.
- Water features: Africa is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Indian Ocean to the east, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north. The continent is also home to several large rivers, including the Nile, the Congo, the Niger, and the Zambezi. Africa has several large lakes as well, such as Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika, and Lake Malawi.
- Climate: Africa has a tropical climate in most regions, with temperatures and precipitation varying widely depending on the location. The equatorial regions have high temperatures and heavy rainfall, while the northern and southern regions are generally drier.
- Vegetation: Africa has a variety of vegetation types, ranging from lush rainforests to savannas and deserts. The continent is home to several iconic species of trees, such as baobabs and acacias, as well as a wide variety of other plant life.
Geographical Location of Africa
- Latitude: Africa is located between approximately 37 degrees north (Cape Blanc, Tunisia) and 35 degrees south (Cape Agulhas, South Africa).
- Longitude: Africa is located between approximately 18 degrees west (Ras Nouadhibou, Mauritania) and 51 degrees east (Ras Hafun, Somalia).
- Geographic center: The geographic center of Africa is approximately 6 degrees north latitude and 18 degrees east longitude, located in the Central African Republic.
- Prime Meridian: The prime meridian (0 degrees longitude) passes through the city of Greenwich, England, which is not located in Africa. However, some African countries use the prime meridian as their reference for time zones, such as Ghana and Mali.
- Tropics: Africa is located within the tropics, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through the northernmost part of the continent and the Tropic of Capricorn passing through the southernmost part.
Historical Significance of Africa
- The emergence of early human species in Africa, including the evolution of Homo sapiens and the development of tools and language.
- The rise of ancient civilizations in Africa, such as Egypt, Nubia, and Ethiopia, which developed advanced systems of writing, architecture, and trade.
- The colonization of Africa by European powers in the 19th and early 20th centuries, which had a profound impact on African societies, economies, and political systems.
- The struggle for independence and decolonization in the mid-20th century, which led to the establishment of many independent African nations.
- The ongoing challenges and opportunities facing Africa today, including issues related to poverty, inequality, conflict, and economic development.
Top 5 places to visit in africa
| Place | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Masai Mara National Reserve | Kenya | Known for its incredible wildlife, including the “Big Five” (lions, elephants, leopards, buffalo, and rhinos). |
| Victoria Falls | Zambia/Zimbabwe | One of the largest waterfalls in the world, located on the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe. |
| Pyramids of Giza | Egypt | Ancient pyramids that have been standing for over 4,500 years, located on the outskirts of Cairo. |
| Cape Town | South Africa | A vibrant coastal city known for its natural beauty, cultural attractions, and excellent food and wine. |
| Serengeti National Park | Tanzania | Another incredible wildlife destination, home to the largest migration of land animals on the planet. |
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Africa:
-
What is the largest country in Africa by land area?
- Algeria is the largest country in Africa by land area, covering approximately 2.38 million square kilometers.
-
What is the most spoken language in Africa?
- There are over 2,000 languages spoken in Africa, but the most widely spoken language is Arabic, followed by Swahili, Hausa, and English.
-
What is the population of Africa?
- As of 2021, the population of Africa is estimated to be around 1.3 billion people.
-
What are some popular tourist destinations in Africa?
- Some popular tourist destinations in Africa include the pyramids of Egypt, the Masai Mara National Reserve in Kenya, Victoria Falls on the border of Zambia and Zimbabwe, and Cape Town in South Africa.
-
What is the economy of Africa like?
- The economy of Africa is diverse, with some countries having strong natural resource industries, while others rely heavily on agriculture or services. Overall, the African economy has seen growth in recent years, but there are still significant challenges related to poverty, inequality, and political instability in some areas.
-
What are some of the major challenges facing Africa?
- Some of the major challenges facing Africa include poverty, inequality, political instability, conflict, and climate change. These issues are complex and interconnected, and require coordinated efforts from governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders to address effectively.